I.
The
amount of GDP desired by private, public, or foreign sector to be purchased at
each possible price level
II. 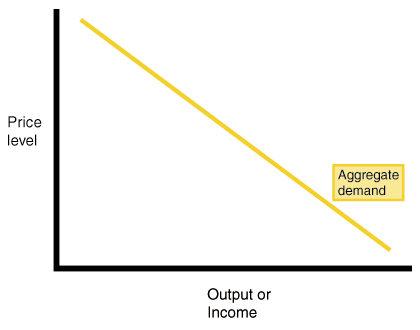

a.
AD
: aggregate demand = C + I + G + X = GDP
b.
PL:
Price level
III.
They're
inverse
a.
Wealth
effect: higher price= lower purchasing power
b.
Interest
effect: higher prices require higher interest rates which discourage spending
and loans.
c.
Foreign
trade (build the wall): higher prices = exports fall and imports rise (unless
you build the wall)
IV.
Shifts
can be
a.
Change
in GDP
b.
Multiplier
effect
c.
Increase
in AD = AD -->
d.
Decrease
in AD= AD <--
V.
Determinants:
a.
Δ
consumption
i.
Consumer
wealth
ii.
Consumer
expectations
iii.
Household
indebtedness
iv.
Taxes
b.
Δ
investment spending
i.
Real
interest rate
ii.
Future
business expectations
iii.
Productivity
and technology
iv.
Business
tax
c.
Δ
Government spending
i.
War
(good)
ii.
Nationalized
health care (bad)
iii.
Decrease
in defense spending
iv.
Spending
increase = AD -->
v.
Spending
decrease = AD <--
d.
Δ
net exports
i.
Exchange
rates
Very good notes, Mr. Ethan Blanchard, they are all very detailed. I think you should add another example of change in exports. You could put National Income compared to abroad. Great blog, love the very descriptive video!
ReplyDelete